HTTP/2
Keypoint: Http/2 aims to improves performance and enables ‘Full-duplex’
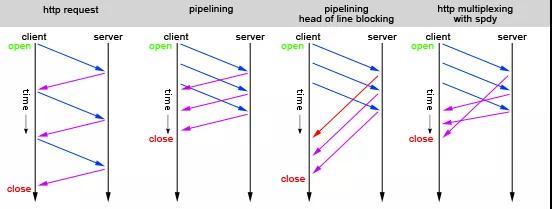
HTTP/1.1 is not efficient when used for HTML web browser. By the nature of TCP’s slow start, each TCP connection will start transmation with a small buffer and slow speed and eventually increase it’s throughput. Such design favors the long connection against short connection. Http/1.1 start a new TCP for each small piece of its web asset, hence on average, those small assets are transfered at a lower speed during “TCP Slow Start”.
HTTP/1.1 is textual. Plantext is human-friendly but less space efficient to wire.
Http/1.1 is monodirectional, it’s always the client to initialize a connection, and service response passively. A downside performance bottleneck is Web client has to parse previous response before starting a new pull request to get the content/asset in previouse response.
Features in Http/2.0
- HTTP/2 is binary protocol where HTTP1.x is textual
- HTTP/2 is multiplexed to tackle a known limitation in networking known as head-of-line blocking
- HTTP/2 use header compression to reduce overhead.
- HTTP/2 Server Push allows servers to proactively send response into client caches.
WebSocket
WebSocket is at the same OSI layer with HTTP. Unlike HTTP, WebSocket provides full-duplex communication.[2][3] Additionally, WebSocket enables streams of messages on top of TCP.
With HTTP/2 you can have multiple streams multiplexed over the same connection. This need to be handled by application developer or a library when using Websocket - if desired.
gRPC
gRPC is an API/Protocol on top of HTTP/2
Head of line block
HTTP / 1.1 to achieve a plurality of requests transmitted by the disposable conduit pipelining techniques in order to increase throughput and performance, such as sequence 2 in the figure above. However, this technique upon receiving the response, requirements must be returned in order of transmission requests. If the first request is blocked, even if the request is later processed, the need to wait, as the above figure 3 sequence.